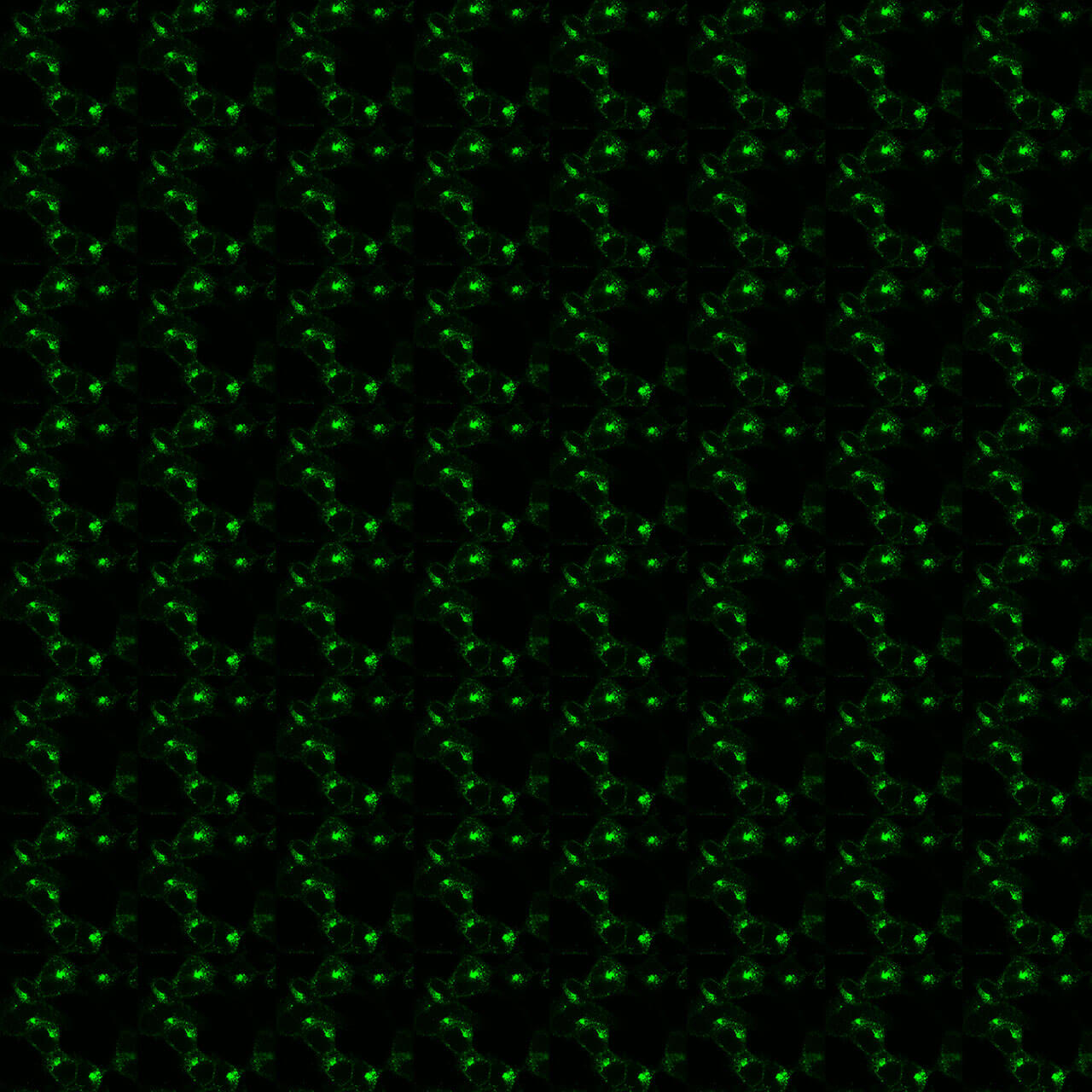
LPA3 Receptor Antibodies
For more information on LPA3 pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database. For further reading refer to:
Chun J, Hla T, Lynch KR, Spiegel S, Moolenaar WH. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXVIII. Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature. Pharmacol Rev. 2010 Dec;62(4):579-87. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003111. PMID: 21079037; PMCID: PMC2993255.
Kihara Y, Maceyka M, Spiegel S, Chun J. Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature review: IUPHAR Review 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Aug;171(15):3575-94. doi: 10.1111/bph.12678. Epub 2014 Jul 12. PMID: 24602016; PMCID: PMC4128058.
Blaho V, Chun J, Herr D, Jones D, Jonnalagadda D, Kihara Y. Lysophospholipid (S1P) receptors in GtoPdb v.2023.1. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology CITE. 2023; 2023(1).
 LPA3 (non-phospho), Lysophosphatidic Acid...
LPA3 (non-phospho), Lysophosphatidic Acid...